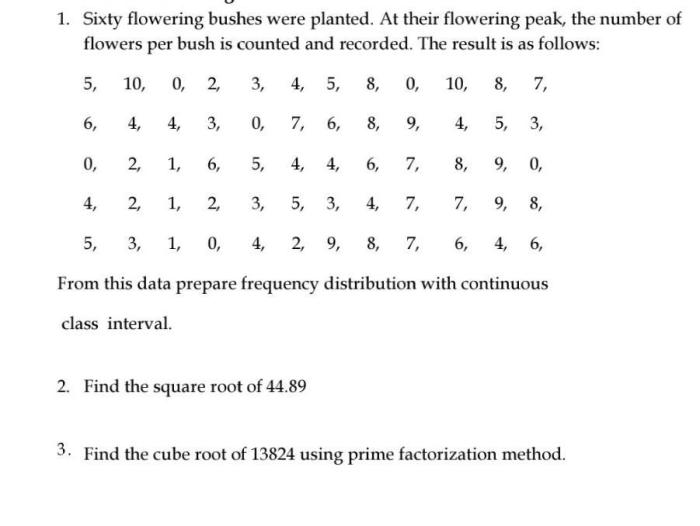
Sixty flowering plants are planted in a flowerbed, a testament to the beauty and diversity of the plant kingdom. This captivating display of colors, textures, and scents transforms the landscape into a living work of art, offering a feast for the senses.
The flowerbed’s design is a symphony of horticultural principles, where each plant is carefully chosen for its seasonality, bloom time, color, and height. The result is a harmonious tapestry that changes with the seasons, providing year-round visual interest.
Plant Species and Varieties
The flowerbed features a diverse selection of sixty flowering plant species, carefully chosen to provide a continuous display of color and interest throughout the year. These species represent a wide range of bloom times, heights, and colors, ensuring that the flowerbed remains vibrant and visually appealing from early spring to late autumn.
- Spring-blooming species:Daffodils, tulips, hyacinths, crocuses, and pansies.
- Summer-blooming species:Roses, lilies, daisies, sunflowers, and zinnias.
- Fall-blooming species:Asters, chrysanthemums, marigolds, and sedums.
The selection of these particular species was guided by several factors, including their adaptability to the local climate, their ease of care, and their ability to attract pollinators. The diverse range of species also ensures that the flowerbed provides a variety of food sources and habitats for wildlife.
Flowerbed Design and Layout

The flowerbed is designed in a formal style, with a symmetrical layout and geometric patterns. It is rectangular in shape, measuring 10 feet by 15 feet, and is divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant features a different color scheme, with warm colors (reds, oranges, and yellows) in the north and south quadrants, and cool colors (blues, purples, and greens) in the east and west quadrants.
The principles of flowerbed design used in the creation of this flowerbed include:
- Color theory:The use of complementary and contrasting colors to create visual interest and harmony.
- Texture contrast:The use of plants with different leaf textures to add depth and dimension to the flowerbed.
- Plant height variation:The use of plants of varying heights to create a sense of movement and drama.
Planting and Maintenance
The flowerbed was planted in the spring, after the last frost. The soil was prepared by adding compost and fertilizer, and the plants were spaced according to their individual needs. The flowerbed is watered regularly, especially during hot and dry weather.
It is also fertilized monthly during the growing season.
The flowerbed requires ongoing maintenance to keep it looking its best. This includes deadheading spent flowers, removing weeds, and pruning plants as needed. The flowerbed is also treated with organic pest control methods to prevent damage from insects and diseases.
Aesthetic Impact and Visual Appeal: Sixty Flowering Plants Are Planted In A Flowerbed
The flowerbed is a focal point of the landscape, and its vibrant colors and diverse plant life create a stunning visual display. The flowerbed is designed to provide interest and beauty throughout the year, with each season bringing its own unique charm.
The flowerbed also contributes to the overall landscape design by providing a splash of color and texture, and by attracting wildlife.
The flowerbed is a popular spot for visitors to relax and enjoy the beauty of nature. It is also used for educational purposes, as it provides a living example of the principles of flowerbed design and plant care.
Environmental Considerations

The flowerbed provides several environmental benefits, including:
- Pollinator habitat:The diverse range of flowering plants attracts a variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds.
- Wildlife habitat:The flowerbed provides food and shelter for a variety of wildlife, including birds, rabbits, and squirrels.
- Water conservation:The use of drought-tolerant plants and organic mulches helps to conserve water.
- Organic gardening:The flowerbed is maintained using organic gardening practices, which helps to protect the environment and human health.
The flowerbed is a valuable addition to the landscape, not only for its beauty but also for its environmental benefits.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of the flowerbed?
The flowerbed serves multiple purposes, including enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the landscape, providing a habitat for pollinators, and showcasing the diversity of flowering plants.
How were the plants selected for the flowerbed?
The plants were carefully selected based on their seasonality, bloom time, color, and height to ensure year-round visual interest and harmony in the overall design.
What maintenance is required for the flowerbed?
The flowerbed requires regular watering, fertilizing, and pest control to maintain its health and beauty. Pruning and deadheading may also be necessary to encourage continued blooming and prevent disease.