Consider a quadratic equation with integer coefficients, a topic that delves into the intriguing world of polynomials, offering a profound understanding of their properties and applications. This equation, expressed in the standard form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts that we shall explore with meticulous precision and captivating insights.
In this discourse, we will embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of quadratic equations, delving into their diverse methods of solution, examining their inherent properties, and uncovering their multifaceted applications across various scientific and practical domains. Prepare to be captivated as we illuminate the enigmatic nature of these equations, revealing their elegance and power.
Quadratic Equation Overview: Consider A Quadratic Equation With Integer Coefficients

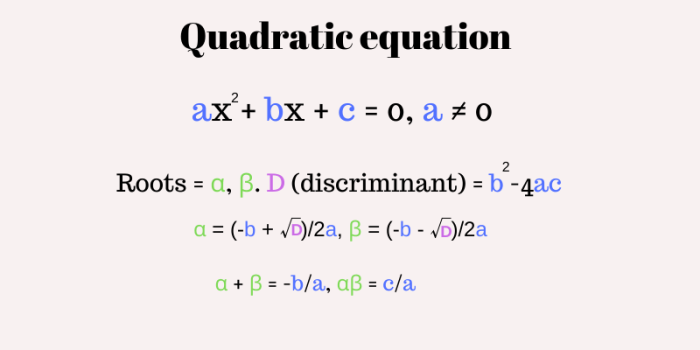
Quadratic equations with integer coefficients are mathematical equations that take the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are integers and a ≠ 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is used to simplify calculations and facilitate analysis.
Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations
Factoring
- Find two numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac.
- Rewrite the middle term using these two numbers.
- Factor by grouping and solve for x.
Quadratic Formula
1. Use the formula
x = (-b ± √(b^2
- 4ac)) / 2a
- Plug in the values of a, b, and c from the equation.
- Solve for x.
Completing the Square
- Move the constant term to the other side of the equation.
- Divide both sides by the coefficient of x^2.
- Add (b/2a)^2 to both sides.
- Factor the left side as a perfect square trinomial.
- Take the square root of both sides.
- Solve for x.
Properties of Quadratic Equations
DiscriminantThe discriminant, D = b^2
4ac, determines the nature of the roots
D > 0
Two distinct real roots
D = 0
One real root (double root)
D < 0
Two complex roots
Relationship between Coefficients and Roots
The sum of the roots
b/a
The product of the roots
c/a
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Real-World Problems
- Projectile motion
- Optimization problems
- Geometric constructions
Science, Engineering, and Business
- Electrical circuits
- Fluid dynamics
- Finance
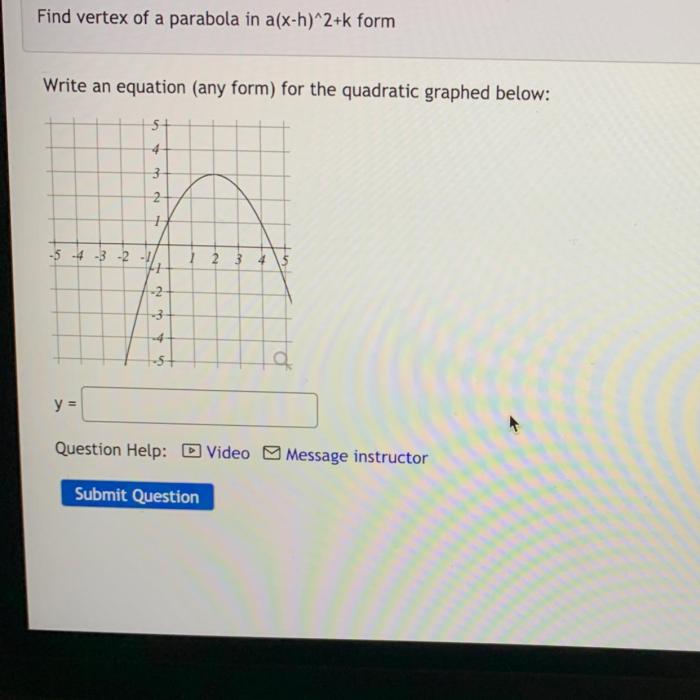
Visual Representations of Quadratic Equations, Consider a quadratic equation with integer coefficients
Interactive GraphAn interactive graph can demonstrate the relationship between the coefficients and the shape of the parabola.
FAQ Resource
What is the standard form of a quadratic equation with integer coefficients?
The standard form is ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are integers.
How do you solve a quadratic equation using factoring?
Factor the quadratic expression into two binomials, set each factor equal to zero, and solve for x.
What is the discriminant, and what does it tell us about the roots of a quadratic equation?
The discriminant is b^2 – 4ac. It determines the nature of the roots: positive discriminant indicates two distinct real roots, zero discriminant indicates one real root, and negative discriminant indicates two complex roots.